The general idea behind the ball mill is an ancient one that was used for grinding flint for pottery. A pharmaceutical ball mill is a type of grinder used to grind and blend materials while manufacturing various dosage forms. The size reduction is done by impact as the balls drop from near the top of the shell. Ball mills are used primarily for single-stage fine grinding, regrinding, and as the second stage in two-stage grinding circuits. According to the need ball mill can be either for wet or dry designs. Ball mills have been designed in standard sizes of the final products between 0.074 mm and 0.4 mm in diameter.
Principle of Ball Mill:
The size reduction in the ball mill is a result of fragmentation mechanisms (impact and attrition) as the balls drop from near the top of the shell. Mixing of feed is achieved by the high energy impact of balls. The energy levels of balls are as high as 12 times the gravitational acceleration. Rotation of base plate provides the centrifugal force to the grinding balls and independent rotation of shell to make the balls hit the inner wall of the shell. Since the shell is rotating in alternate (one forward cycle and one reverse cycle) directions a considerable part of grinding takes place in addition to homogenous mixing. The operating principle of the ball mill consists of the following steps. In a continuously operating ball mill, the feed material is fed through the central hole into the drum (shell) and moves there along with grinding media (balls).
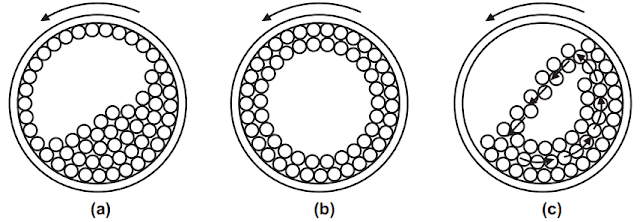 |
| Fig.1: Cascade Operation in Ball Mill (a) Low Speed (b) High Speed (c) Correct Speed |
The material to be ground is fed from a hopper at a 60° angle and the product is discharged through a 30° angle. As the shell rotates the balls are lifted on the rising side of the shell and cascade down (or drop down onto the feed) from near the top of the shell. The material grinding occurs during the impact of falling grinding balls and abrasion of the particles between the balls. The discharge of ground material is performed through the central hole in the discharge cap (mills with center unloading the milled product) or through the grid (mills with unloading the milled product through the grid). In the ball mill depending on the rotational speed following possible modes of the grinding media motion could be achieved.
- Low speed: Speed mode with a rolling of grinding balls without flight.
- Mixed mode (Cascade mode motion): Speed mode with a partial rolling and a partial flight of grinding balls.
- High speed: Speed mode with the circular motion of balls with no fall.
In ball
milling, the speed of the rotation is more important. At a low speed, Fig.1(a),
the mass of the ball slides or rolls over each other with inefficient output.
At a high speed, Fig.1(b), the balls are thrown out to the walls by centrifugal
force. Since at this speed there is the absence of any impact or attrition no
grinding occurs. Compression by the ball against the shell wall is not enough
for comminution. But at 2/3rd of the speed (50 to 80% of the critical speed),
Fig.1(c), the centrifugal speed force just occurs with the result that the
balls are carried almost to the top of the mill and then fall to the bottom. In
this way, the maximum size reduction is affected by the impact of particles
between the balls and by attrition between the balls. After a suitable time,
the material is taken out and passed through a sieve to get powder of the
required size. Ball mills are very effective for grinding smooth, aqueous, or
oily dispersions by wet grinding since it gives particles of 10 microns or
less.
Construction of Ball Mill:
The basic
parts of the ball mill are a shell, balls, and motor Fig.2. A ball mill is also
known as a pebble mill or tumbling mill. It consists of a hollow cylindrical
shell (drum) containing balls mounted on a metallic frame such that it can be
rotated along its longitudinal axis. The axis of the shell may be either
horizontal or at a small angle to the horizontal. It is partially filled with
balls. The grinding media is the balls, which may be made of chrome steel,
stainless steel, or ceramic. The balls which could be of different diameters
occupy 30 - 50% of the mill volume and its size depends on the feed and mill
size. The large balls tend to break down the coarse feed materials and the
smaller balls help to form the fine product by reducing void spaces between the
balls. Usually, the grinding media ball's weight is kept constant. The ball
size depends on the feed and the diameter of the mill. The inner surface of the
cylindrical shell is usually lined with an abrasion-resistant material such as
manganese steel or rubber. Less wear takes place in rubber-lined mills. The
metallic cylinder which is coated with different materials is helpful in the
mechanism of attrition. The length of the mill is approximately equal to or
slightly greater than its diameter.
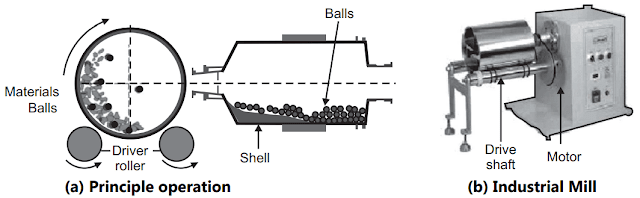 |
| Fig.2: Pharmaceutical Ball Mill |
An
internal cascading effect reduces the material to a fine powder. Industrial
ball mills can operate continuously to be fed at one end and discharged at the
other. Large to medium ball mills are mechanically rotated on their axis, but
small ones normally consist of a cylindrical capped container that sits on two
drive shafts. High-quality ball mills are potentially expensive and can grind
mixture particles to as small as 0.0001 mm, enormously increasing surface area
and reaction rates.
Factors determining the efficiency of ball mill:
The degree of milling in a ball mill is influenced by;
- The residence time of the material in the mill chamber.
- The size, density, and the number of the balls.
- The nature (hardness) of the balls and material to be grinded.
- Feed rate and feed level in the vessel.
- Rotation speed of the cylinder.
Working of Ball Mill:
Several types of ball mills exist. They differ to an extent in their operating principle. They also differ in their maximum capacity of the milling shell, ranging from 0.010 liters for planetary ball mill, mixer mill, or vibration ball mill to several 100 liters for horizontal rolling ball mills. The steps involved in the working process of ball mill are as follows:
- Initial stage: The powder particles are get flattened by the collision of the balls. It leads it changes in the shapes of individual particles or clusters of particles being impacted repeatedly by the milling balls with high kinetic energy.
- Intermediate stage: Significant changes occur in comparison with those in the initial stage.
- Final stage: Reduction in particle size takes place. The microstructure of the particle also appears to be more homogenous on a microscopic scale than those at the initial and intermediate stages.Completion stage: The powder particles possess an extremely deformed metastable structure.
Types of Ball Mill:
There are various types of ball mills used for different applications amongst which the first two are commonly used in pharmaceutical practice. These include Pebble ball mill, Vibrating ball mill, Drum ball mills, Jet-mills, Bead-mills, Horizontal rotary ball mills,
- Pebble ball mill: Pebble mills are sometimes called jar mill or pot mill which works on the principle of attrition and impact. The grinding is effected by placing the substance in the cylindrical vessel or jar vessels that are lined by porcelain or other hard substance containing pebbles or balls. The cylindrical vessel revolves horizontally on their long axis and the tumbling of the pebbles over one another and against the sides of the cylinder produce pulverization with a minimum loss of material.
- Vibrating ball mill: Vibrating ball mill also works on the principle of attrition and impact. It consists of a mill shell containing a charge of balls similar to that of ball mills. In this case, the shell vibrates due to some frequency rather than rotated.
Uses of Ball Mill:
- Small capacity ball mills are used for the final grinding of drugs or grinding suspensions.
- The high-capacity ball mills are used for milling ores before the manufacture of pharmaceutical chemicals.
- Ball mills are an efficient tool for grinding many brittle and sticky materials into fine powder.
- The hard and abrasive as well as wet and dry materials can be grinded in the ball mills for pharmaceutical purposes.
- Powders for ophthalmic and parenteral products can be reduced in size.
- Ball mill is used for the milling of pigments and insecticides for industrial purposes.
- Ball mills are also used in the manufacture of black powder.
- The blending of explosives is an example of an application for rubber balls.
- For systems with multiple components, ball milling is effective in increasing solid-state chemical reactivity.
- Ball milling has been shown effective for the production of amorphous materials.
Advantages of Ball Mill:
- It produces very fine powder (particle size less than or equal to 10 microns).
- It is suitable for milling toxic materials because of its design as a completely enclosed form.
- It is used in milling highly abrasive materials.
- Strong adaptability to the fluctuation of the physical property of the materials such as granularity, water content, and hardness.
- Ball mill has a big crushing ratio and high production capacity.
- It has a simple design, ease of examination, and change of abraded spare parts.
- Reliable operation, simple maintenance, and management.
- It can be used for continuous operation if a sieve or classifier is attached to the mill.
- It is capable of grinding a large variety of materials of different characters and different degrees of hardness.
- It is suitable for wet as well as dry grinding processes.
- The cost of installation, power, and grinding medium is low.
- It is suitable for both batch and continuous operation.
- Suitable for grinding material with high hardness.
- The shape of the final products is circular.
- No contamination in the powder with ceramic ball.
- The capacity and fineness can be adjusted by adjusting the diameter of the ball.
Disadvantages of Ball Mill:
- Contamination of product may occur as a result of wear and tear of the balls and partially from the casing.
- High machine noise level especially if the hollow cylinder is a mode of metal, but much less if the rubber is used.
- It has a relatively long milling time due to low rotary speed and thus has low working efficiency.
- It is difficult to clean the machine after use.
- High production cost and high unit electricity consumption.
- Heavy equipment so very high one-time capital investment.
- Some raw materials may become damaged by steel balls.
- Not suitable for sensitive and flammable substances.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : hammer mill